Bubble sort is a sorting algorithm that compares two adjacent elements and swaps them until they are in the intended order.
Imagine you have a set of numbered cards that are all mixed up. With bubble sort, you start at one end and look at pairs of cards. If a card with a smaller digit is in front of a card with a larger number, you swap their places.
It’s called “bubble” sort because, this is like bubbles rising in water, the smaller numbers gradually move upwards in the list, each one finding its way to the correct place.
This keeps occurring until all the cards are in order—just like when all the bubbles reach the water’s surface, and everything’s resolved. That’s bubble sort algoritham
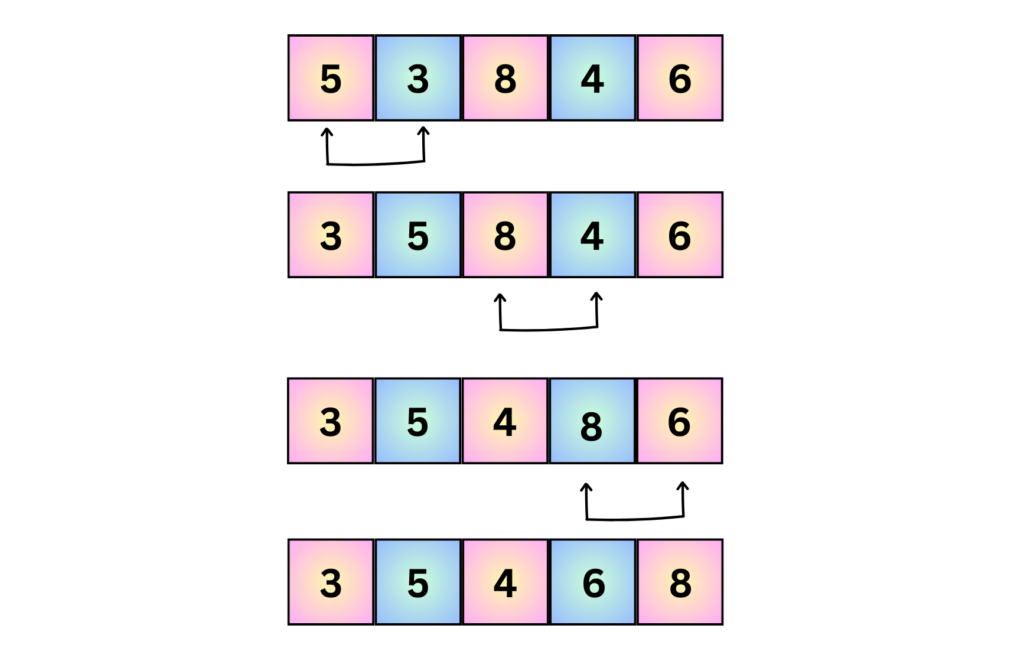
Table of Contents
Bubble Sort Algorithm
bubbleSort(array)
for i <- 1 to indexOfLastUnsortedElement-1
if leftElement > rightElement
swap leftElement and rightElement
end bubbleSort# Bubble sort in Python
def bubbleSort(array):
# loop to access each array element
for i in range(len(array)):
# loop to compare array elements
for j in range(0, len(array) - i - 1):
# compare two adjacent elements
# change > to < to sort in descending order
if array[j] > array[j + 1]:
# swapping elements if elements
# are not in the intended order
temp = array[j]
array[j] = array[j+1]
array[j+1] = temp
data = [-2, 45, 0, 11, -9]
bubbleSort(data)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)This is just a placeholder to help you visualize how the content is displayed in the tabs. Feel free to edit this with your actual content.
bubbleSort(array)
for i <- 1 to indexOfLastUnsortedElement-1
if leftElement > rightElement
swap leftElement and rightElement
end bubbleSortBubble Sort Code in Python, Java and C/C++
# Bubble sort in Python
def bubbleSort(array):
# loop to access each array element
for i in range(len(array)):
# loop to compare array elements
for j in range(0, len(array) - i - 1):
# compare two adjacent elements
# change > to < to sort in descending order
if array[j] > array[j + 1]:
# swapping elements if elements
# are not in the intended order
temp = array[j]
array[j] = array[j+1]
array[j+1] = temp
data = [-2, 45, 0, 11, -9]
bubbleSort(data)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)// Bubble sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class Main {
// perform the bubble sort
static void bubbleSort(int array[]) {
int size = array.length;
// loop to access each array element
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++)
// loop to compare array elements
for (int j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++)
// compare two adjacent elements
// change > to < to sort in descending order
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// swapping occurs if elements
// are not in the intended order
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { -2, 45, 0, 11, -9 };
// call method using class name
Main.bubbleSort(data);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}// Bubble sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
// perform the bubble sort
void bubbleSort(int array[], int size) {
// loop to access each array element
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; ++step) {
// loop to compare array elements
for (int i = 0; i < size - step - 1; ++i) {
// compare two adjacent elements
// change > to < to sort in descending order
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
// swapping occurs if elements
// are not in the intended order
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// print array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int data[] = {-2, 45, 0, 11, -9};
// find the array's length
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
bubbleSort(data, size);
printf("Sorted Array in Ascending Order:\n");
printArray(data, size);
}// Bubble sort in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// perform bubble sort
void bubbleSort(int array[], int size) {
// loop to access each array element
for (int step = 0; step < size; ++step) {
// loop to compare array elements
for (int i = 0; i < size - step; ++i) {
// compare two adjacent elements
// change > to < to sort in descending order
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
// swapping elements if elements
// are not in the intended order
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// print array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
cout << " " << array[i];
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main() {
int data[] = {-2, 45, 0, 11, -9};
// find array's length
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
bubbleSort(data, size);
cout << "Sorted Array in Ascending Order:\n";
printArray(data, size);
}Optimized Bubble Sort Algorithm
In this algorithm, all the comparisons are made even if the array is already sorted.
This increases the performance time.
To solve this, we can introduce an additional variable swapped. The value of swapped is set true if there appears swapping of elements. Otherwise, it is set false.
After an iteration, if there is no swapping, the value of swapped will be false. This means elements are already sorted and there is no requirement to perform further iterations.
This will decrease the implementation time and helps to optimize the bubble sort.
bubbleSort(array)
swapped <- false
for i <- 1 to indexOfLastUnsortedElement-1
if leftElement > rightElement
swap leftElement and rightElement
swapped <- true
end bubbleSortOptimized Bubble Sort in Python, Java, and C/C++
# Optimized Bubble sort in Python
def bubbleSort(array):
# loop through each element of array
for i in range(len(array)):
# keep track of swapping
swapped = False
# loop to compare array elements
for j in range(0, len(array) - i - 1):
# compare two adjacent elements
# change > to < to sort in descending order
if array[j] > array[j + 1]:
# swapping occurs if elements
# are not in the intended order
temp = array[j]
array[j] = array[j+1]
array[j+1] = temp
swapped = True
# no swapping means the array is already sorted
# so no need for further comparison
if not swapped:
break
data = [-2, 45, 0, 11, -9]
bubbleSort(data)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)// Optimized Bubble sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class Main {
// perform the bubble sort
static void bubbleSort(int array[]) {
int size = array.length;
// loop to access each array element
for (int i = 0; i < (size-1); i++) {
// check if swapping occurs
boolean swapped = false;
// loop to compare adjacent elements
for (int j = 0; j < (size-i-1); j++) {
// compare two array elements
// change > to < to sort in descending order
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// swapping occurs if elements
// are not in the intended order
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
// no swapping means the array is already sorted
// so no need for further comparison
if (!swapped)
break;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { -2, 45, 0, 11, -9 };
// call method using the class name
Main.bubbleSort(data);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}// Optimized Bubble sort in C
#include
// perform the bubble sort
void bubbleSort(int array[], int size) {
// loop to access each array element
for (int step = 0; step < size - 1; ++step) {
// check if swapping occurs
int swapped = 0;
// loop to compare array elements
for (int i = 0; i < size - step - 1; ++i) {
// compare two array elements
// change > to < to sort in descending order
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
// swapping occurs if elements
// are not in the intended order
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = temp;
swapped = 1;
}
}
// no swapping means the array is already sorted
// so no need for further comparison
if (swapped == 0) {
break;
}
}
}
// print array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// main method
int main() {
int data[] = {-2, 45, 0, 11, -9};
// find the array's length
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
bubbleSort(data, size);
printf("Sorted Array in Ascending Order:\n");
printArray(data, size);
}// Optimized bubble sort in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// perform bubble sort
void bubbleSort(int array[], int size) {
// loop to access each array element
for (int step = 0; step < (size-1); ++step) {
// check if swapping occurs
int swapped = 0;
// loop to compare two elements
for (int i = 0; i < (size-step-1); ++i) {
// compare two array elements
// change > to < to sort in descending order
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
// swapping occurs if elements
// are not in intended order
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = temp;
swapped = 1;
}
}
// no swapping means the array is already sorted
// so no need of further comparison
if (swapped == 0)
break;
}
}
// print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
cout << " " << array[i];
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main() {
int data[] = {-2, 45, 0, 11, -9};
// find the array's length
int size = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
bubbleSort(data, size);
cout << "Sorted Array in Ascending Order:\n";
printArray(data, size);
}Bubble Sort Complexity
| Time Complexity | |
|---|---|
| Best | O(n) |
| Worst | O(n2) |
| Average | O(n2) |
| Space Complexity | O(1) |
| Stability | Yes |
Complexity in details
Bubble Sort Compares the adjacent elements
| Cycle | Number of Comparisons |
|---|---|
| 1st | (n-1) |
| 2nd | (n-2) |
| 3rd | (n-3) |
| ……. | …… |
| last | 1 |
Hence, the umber of comparision is
(n-1) + (n-2) + (n-3) +.....+ 1 = n(n-1)/2
nearly equals to n2
Hence, Complexity O(n2)
Also, if we observe the code, bubble sort requires two loops. Hece, the complexity is n*n = n2
1. Time Complexities
- Worst Case Complexity:
O(n2)
If we want to sort in ascending order and the array is in descending order then the worst case occurs. - Best Case Complexity:
O(n)
If the array is already sorted, then there is no need for sorting. - Average Case Complexity:
O(n2)
It occurs when the elements of the array are in jumbled order (neither ascending nor descending).
2. Space Complexity
- Space complexity is
O(1)because an extra variable is used for swapping. - In the optimized bubble sort algorithm, two extra variables are used. Hence, the space complexity will be
O(2).
Bubble Sort Applications
Bubble sort is used if
- complexity does not matter
- short and simple code is preferred



1 thought on “Bubble Sort”
Comments are closed.